Introduction - PRSTools#
Background#
While working on a manuscript focused on benchmarking machine learning algorithms for genotype-phenotype prediction, I received feedback recommending the inclusion of a broader analysis of PRS methodologies. This led me to investigate various PRS calculation tools used in genetic research, each of which applies unique approaches and assumptions that influence final PRS. These findings were supported by studies like this one on PubMed, which reviews the diversity in PRS tools.
The calculation of PRS depends on several factors:
Data Type Compatibility: Some tools rely on GWAS summary statistics, others use genotype data, and some utilize both types.
Modeling Differences: Tools apply different mathematical models, impacting PRS interpretation.
Reference Panels and Genome Builds: PRS tools may require specific reference panels, which affect compatibility and generalizability.
Key Challenges#
Implementing PRS tools for practical analysis posed several challenges:
Data Format Incompatibility: Different tools accept varying input formats, making data integration across tools challenging.
Limited Cross-Validation Support: Many tools lack built-in cross-validation functionality, essential for robust model validation.
HPC Scalability Constraints: Some tools are not optimized for high-performance computing (HPC), limiting scalability for analyses across multiple phenotypes.
Repository Overview#
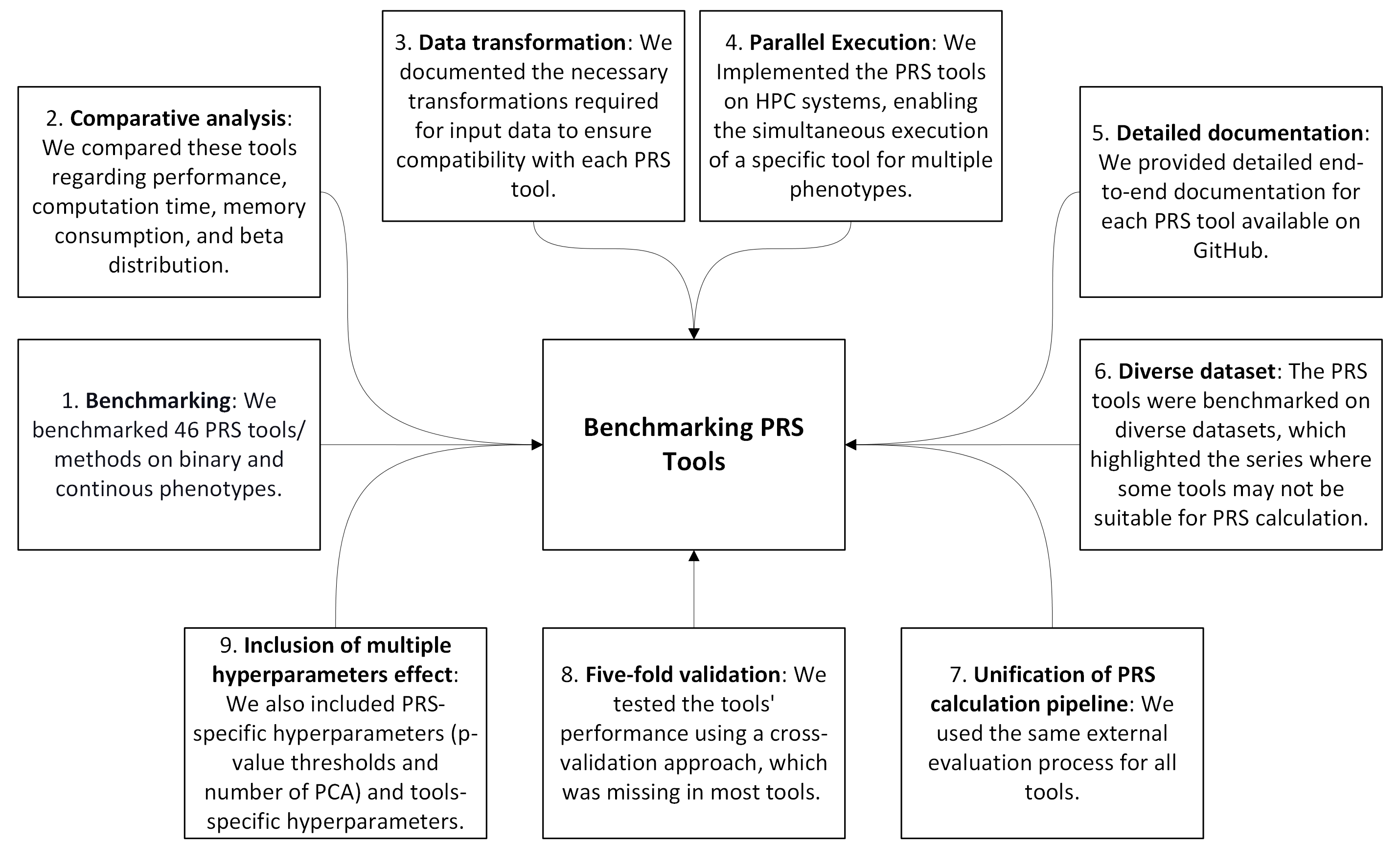
To address these challenges, we created a new repository that provides a unified implementation of PRS calculation tools with enhancements for usability in real-world research settings. Key features include:
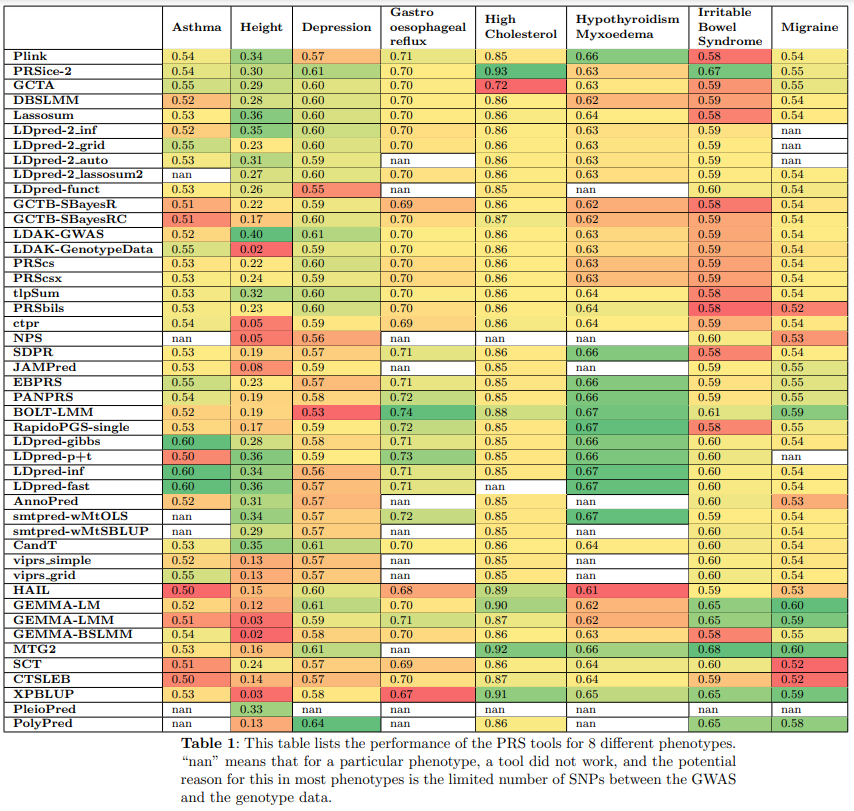
Benchmarking: We benchmarked 46 PRS tools/methods on both binary and continuous phenotypes.
Comparative Analysis: Performance, computation time, memory consumption, and beta distribution of each tool were compared.
Data Transformation: Documentation on the necessary input data transformations ensures compatibility across PRS tools.
Parallel Execution: Tools were implemented for parallel execution on HPC systems, enabling simultaneous analyses across multiple phenotypes.
Detailed Documentation: Comprehensive end-to-end documentation for each PRS tool is available on GitHub.
Diverse Dataset Testing: PRS tools were benchmarked on diverse datasets, revealing specific tools’ limitations for certain data types.
Unified PRS Calculation Pipeline: A standardized evaluation process was applied across all tools.
Cross-Validation Implementation: Five-fold cross-validation was incorporated to assess tool performance, an often-missing feature.
Hyperparameter Tuning: PRS-specific hyperparameters (e.g., p-value thresholds, PCA counts) and tool-specific hyperparameters were included to optimize PRS accuracy.
Conclusion#
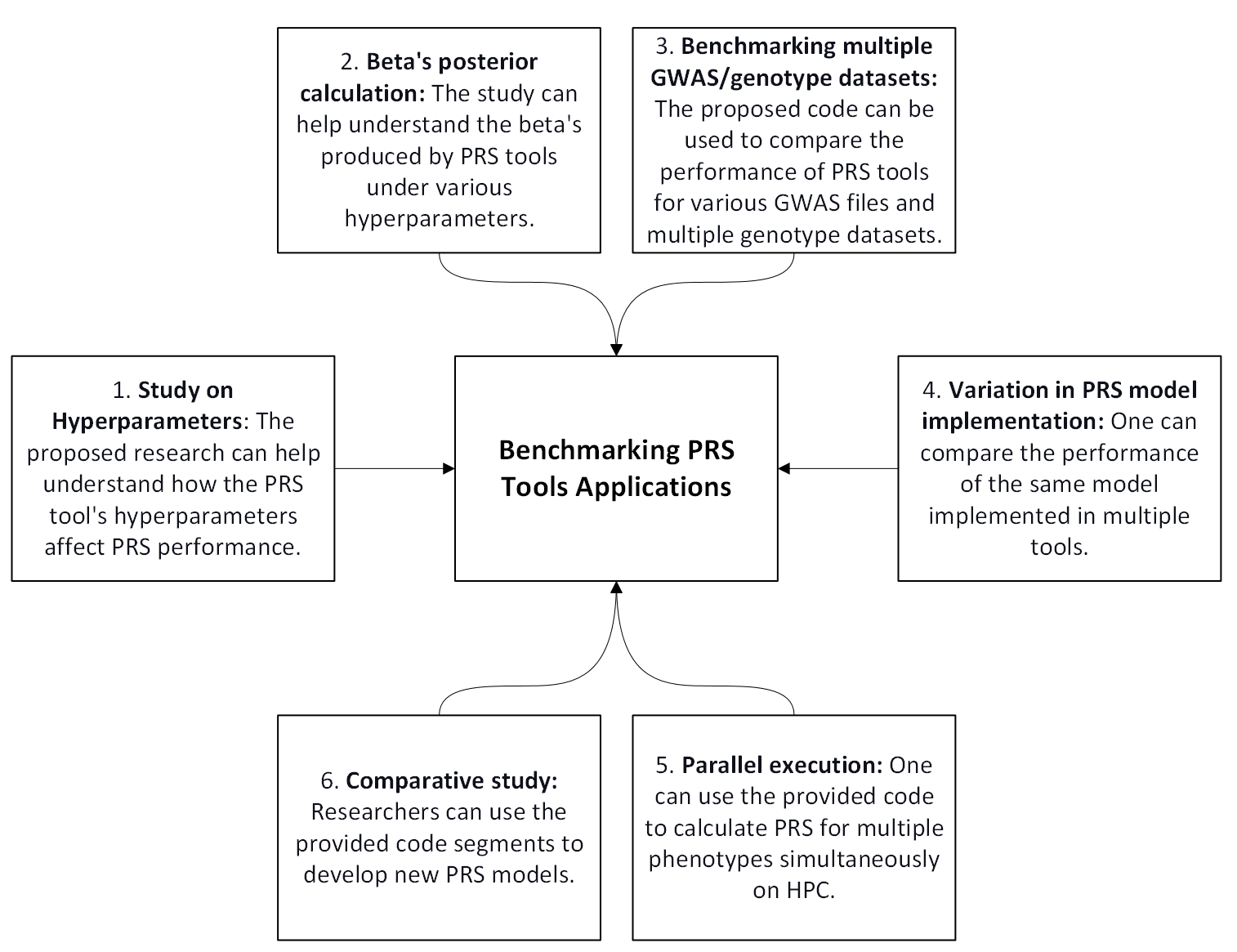
In summary, this repository addresses some limitations in current PRS tools, providing researchers with an adaptable and efficient solution for polygenic risk score calculations. By improving compatibility, scalability, and documentation, the repository supports large-scale genetic studies and promotes broader use of PRS methodologies in research.
PRS Tools Included in the Analysis.#
Following is the list of PRS tools included in the analysis.
Tool |
Python |
Conda Environment |
Tool Link |
Phenotype (Binary/Continuous/Both) |
Requires Genotype data |
Requires GWAS data |
Requires Covariate data |
Requires Reference data |
Dependence |
Language |
Original article DOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Plink |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
C |
||
PRSice-2 |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
Optional |
Optional, but recommended |
No |
C++ and R |
||
GCTA |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
DBSLMM |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
No (optional, can be used as reference panel) |
Yes |
No |
Optional, but recommended |
Plink (PRS calc), LDpred-2 (Heritability calc) |
C++ and R |
||
lassosum |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
ldpred2_inf |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
ldpred2_grid |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
ldpred2_auto |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
ldpred2_lassosum2 |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
ldpred-funct |
2 |
ldscc |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calc), LDpred-2 (Heritability calc) |
Python |
||
SBayesR |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes - To create an LD matrix |
Yes |
No |
Yes - LD Matrix |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
SBayesRC |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes - To create an LD matrix |
Yes |
No |
Yes - LD Matrix |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
LDAK-genotype |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
LDAK-gwas |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes - Correlation Matrix |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
PRScs |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes - LD Matrix |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
PRScsx |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes - LD Matrix |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
tlpSum |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
PRSbils |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
CTPR |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
NPS |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
SDPR |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes - To create an LD matrix |
Yes |
No |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
JAMPred |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
EB-PRS |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
PANPRS |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes - As LD matrix |
Yes |
No |
Yes - LD Matrix |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
BOLT-LMM |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
RapidoPGS-single |
3 |
AdvanceR |
Both |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
LDpred-gibbs |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
LDpred-p+t |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
LDpred-inf |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
LDpred-fast |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
Anno-Pred |
2 |
ldscc |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
smtpred-wMtOLS |
2 |
ldscc |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
smtpred-wMtSBLUP |
2 |
ldscc |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
C+T (Clumping and Thresholding) |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
viprs-simple |
3 |
viprs_env |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
viprs-grid |
3 |
viprs_env |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
HAIL |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
GEMMA-LM |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
GEMMA-LLM |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
GEMMA_BSLMM |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
MTG2 |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
C++ |
||
SCT |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
XP-BLUP |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Bash |
||
CTSLEB |
3 |
genetics |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
R |
||
PolyPred |
3 |
polyfun |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
||
Pleio-Pred |
2 |
ldscc |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Plink (PRS calculation) |
Python |
Conda Environment#
You may need to create the following Conda Environment to execute each file.
advanceR Environment
Download environment.yml
Download replication_instructions.txtgenetics Environment
Download environment.yml
Download replication_instructions.txtldscc Environment
Download environment.yml
Download replication_instructions.txtpolyfun Environment
Download environment.yml
Download replication_instructions.txtviprs_env Environment
Download environment.yml
Download replication_instructions.txt
The following tools were discarded from further consideration for the following reasons:
Multiprs – This methodology calculates PRS for multiple p-value thresholds and then combines them to form a single prediction. It is a methodolgy rather a tool.
BGLR-R – While this software worked with its provided test data, it failed with our data, returning
NaNfor the explained variances across all phenotypes. This was despite our data matching the required format, with no missing genotype values for SNPs or individuals.PolyRiskScore – This is a web-based tool that calculates PRS for specific SNPs and uses GWAS files from the GWAS catalog. Due to its limited flexibility and dependency on specific SNPs, it was not suitable for our needs.
FairPRS – Although promising, this tool writes output files to the same directory, making it incompatible with running multiple phenotypes or datasets simultaneously on HPC. The lack of parallel processing capability led us to exclude it from further consideration.
RapidoPGS-multi – This tool did not support continuous phenotypes, though it worked for binary ones. Due to this limitation, it was removed from further consideration.
Results#